Hello everyone! Hope you all are well. In this post, we are going to understand another useful data structure i.e Hash Table.
Before understanding the Hash Table, we have to understand what is Hashing.
Hashing?
Hashing is a common technique for storing data in such a way that the data can be inserted and retrieved very quickly. Hashing uses a data structure called Hash Table.
What is a Hash Table?
Hash Table is a data structure that stores data in an associative manner. In a hash table, data is stored in an Array format, where each data value has its own unique index value. The array consists of elements 0 through N size, We can increase the size when necessary.
Each data element is stored in the array with an associative key, which is similar to the concept of the key we examined with the dictionary data structure or objects in plain javascript.
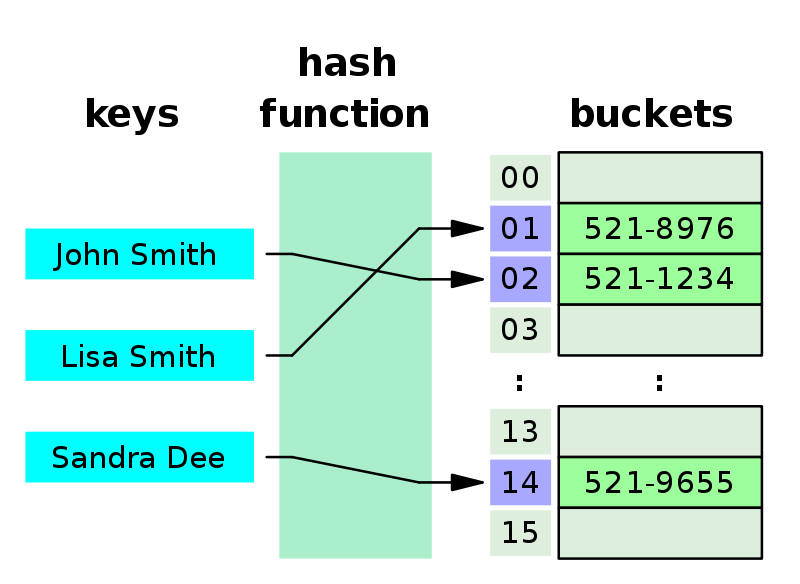
To store data in a hash table, the key is mapped into a number in the range of 0 through the hash table size, using a hash function
Hash Function?
Hash Function is a normal function that is used to generate a hash index value. The purpose of a hash function is to create an index that will be used to reference the value that we want to store. The function accepts the key to be mapped then uses an algorithm to calculate the value of the key to an integer index(also known as hashIndex).
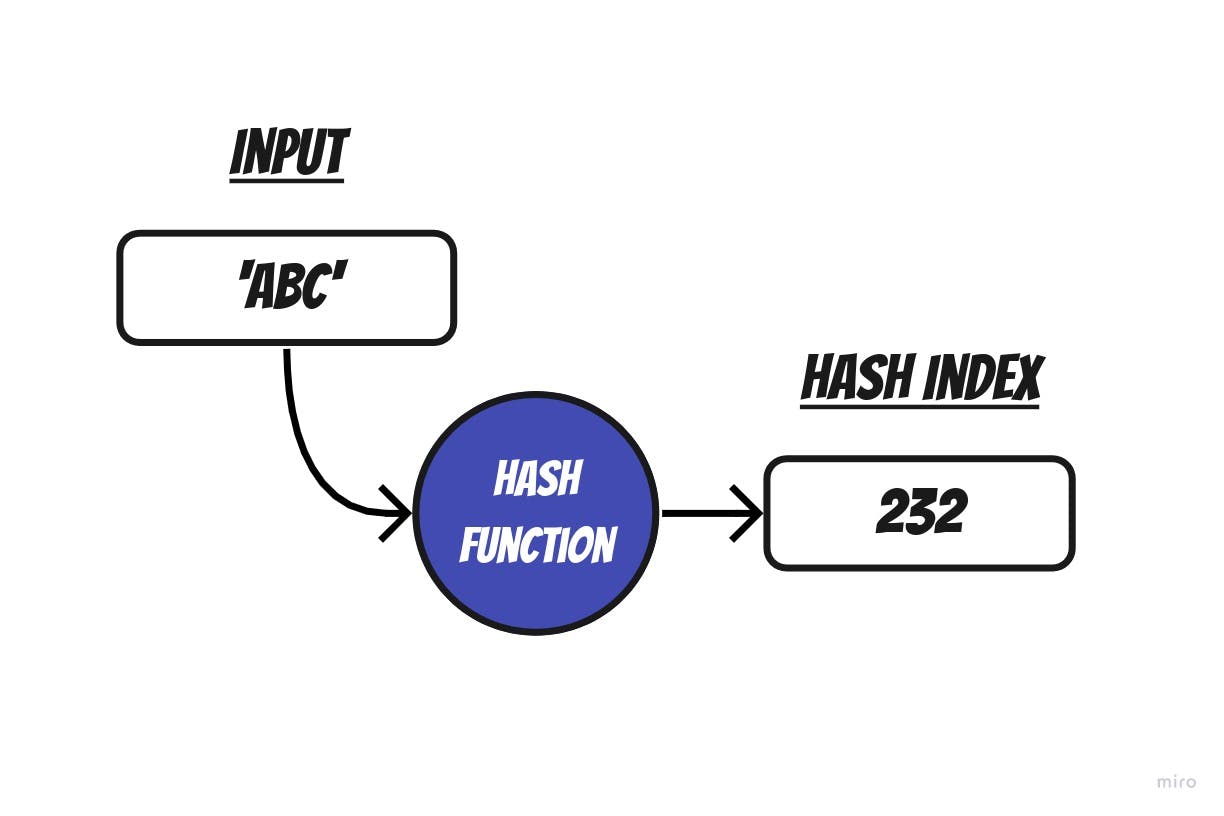
Let k be a key and h be a hash function. Here, h(k) will produce an hashIndex that will be used as an index.
h(k) = hashIndex
There are many algorithms for calculating the hash index. Some of the common methods used are:
Arithmetic Modular
In this approach, we take the modular of the key with the size of the array.
hashIndex = key MOD table_size
Truncation
In this approach, we select a part of the key as the index rather than the whole key. We can use a mod function for this operation, although it does not need to be based on the array size.
Folding
This approach involves dividing the key into small chunks and applying a different arithmetic strategy at each chunk.
Hash Collision
When a hash function generates a same index for multiple keys, it creates a conflict because we have two values for the same index(What value is to be stored in that index). This is called a hash collision.
Avoiding Hash Collision
There are many techniques to handle hash collisions. Some of the most used techniques are:
Chaining
In chaining, if the hash code of the second value is the same index then we replace that index value with an array or linked list. All values pointing to that index are stored in this array/linked list.
If there is only one hash code pointing to an index of the array then the value can be directly stored in that index or for consistency purposes, you can store it inside an array/linked list as well.

Linear Probing
The linear probing technique works on the concept of "keep incrementing until you find an empty slot". If the collision has occurred at the 0th slot, then the next(1st) slot is checked, and so on. In simple words, the value of the index is incremented linearly until and unless the free slot is found.
The pseudo-code looks like this:
index = h(k)
while(val(index) is occupied) # check the availability of slot
index = (index+1) mod n # keep incrementing the index
Double hashing
In this technique, we use two hashing functions h1(k) and h2(k). If the slot at h1(k) is occupied then the second hashing function h2(k) is used to find the next slot.
The pseudo-code looks like this:
index = h1(k)
while(val(index) is occupied)
index = (index + h2(k)) mod n # h2(k) is used to calculate another hash
Time Complexity
| Operation | Average Case | Worst Case |
| Search | O(1) | O(n) |
| Insert | O(1) | O(n) |
| Delete | O(1) | O(n) |
✨ Coding Hash Table in JavaScript
Let's start by creating a HashTable class.
class HashTable {
constructor() {
// the initial size of the table is 300
this.table = new Array(300);
}
}
First, we have to create a hash function. As mentioned there are many algorithms for calculating the hash functions.
NOTE: We are going to use a simpler approach for the scope of this blog. You can always research all the amazing methods for hash functions 😉
Let's write our hash function.
function calculateHashIndex(key, tableSize) {
// pick a random prime number as starting hashIndex
let hashIndex = 7;
// loop over the key
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
// key.charCodeAt(i) will return an ASCII code which is a number
// we will multiply it by hashIndex and another prime number
// % will give us a number in the range between 0 - tableSize
hashIndex = (11 * hashIndex * key.charCodeAt(i)) % tableSize;
}
return hashIndex;
}
Add
The add operation is used to add an item into the hash table.
Here are the steps which we are going to follow for writing the add method:
- Create a new method
addin theHashTableclass that is going to accept two arguments.key- The key that is going to be indexed.value- The value stored against the index.
- Calculate the
hashIndexby using thecalculateHashIndexfunction. - Check if the index already exists?
- If yes, then
pushthe new item on the chained array. - If No, then create a new array of arrays and assign it to index.
- If yes, then
add(key, value) {
// calculate the hasIndex by the provided key and table length
const hashIndex = calculateHashIndex(key, this.table.length);
// check if the index already exist?
if (this.table[hashIndex]) {
// push the value to the current array of elements on that particular index (Chaining Method)
this.table[hashIndex].push([key, value]);
} else {
// if not, then push an array of array to that index (Chaining Method)
this.table[hashIndex] = [[key, value]];
}
}
Search
The search operation is used to add get/search an item from the hash table.
These are the steps which we are going to take for search.
- Create a new method
searchin theHashTableclass that is going to accept one argument that is thekey. - Calculate the
hashIndexby using thecalculateHashIndexfunction. - Check if the index already exists? If No then return
null. - If the key exists, then we have to perform the search operation. Remember, every item in the hash table is an array that is stored against a
hashedIndex. We have already calculated thehashIndexsothis.table[hashIndex]will give us an array of values. We will use thefind()method to find the element.[1]will give us the value.
search(key) {
// calculate the hasIndex by the provided key and table length
const hashIndex = calculateHashIndex(key, this.table.length);
// if the key doesn't exist, return null
if (!this.table[hashIndex]) {
return null;
}
// lookup for the value based on the key
return this.table[hashIndex].find((x) => x[0] === key)[1];
}
Now, Let's make use of our HashTable.
const ht = new HashTable();
ht.add('firstName', 'rehan');
ht.add('lastName', 'sattar');
ht.add('age', 22);
ht.add('dob', '1/01/1111');
console.log(ht.search('firstName')); // rehan
console.log(ht.search('lastName')); // sattar
console.log(ht.search('age')); // 22
console.log(ht.search('dob')); // 1/01/1111
There is one remaining operation i.e Deletion which is easy and your homework 🤭
Try to add deletion functionality in this hash table. This will help you to gain more command over the topic. 🌱
Here is the complete code for this post:
That's it, folks! hope it was a good read for you. Thank you! ✨